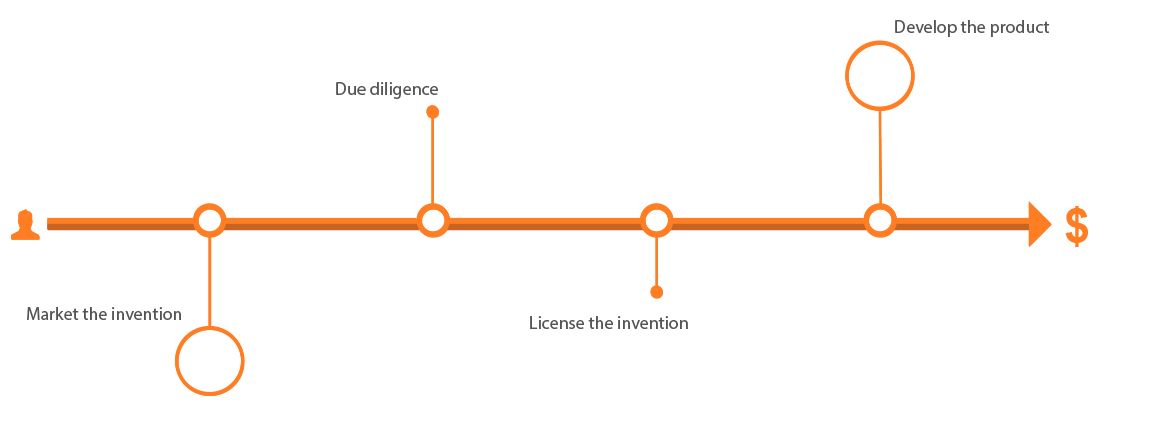
LICENSING PROCESS
Step-by-step instructions
Licensing process
MARKET THE INVENTION
OTC uses the online database Flintbox to allow industry to search available UTEP technologies. We also attend conferences and industry events to promote our technology. Once interests are identified, we will work together with the inventors to describe the technical details and advantages of the invention to potential licensee under a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA).
DUE DILIGENCE
Potential licensees are strongly suggested to conduct their own due diligence before entering into a licensing discussion with OTC. Here are some of the key questions:- Evaluate the intellectual property proposed to be licensed and its potential value to your business.
- Can you develop the intellectual property independently without infringing?
- Is a patent likely to be issued? How strong is the patent?
- Will you need additional intellectual property protection around the patented technology and can you acquire it?
OTC does not guarantee a patent will ever issue and it is up to the licensee to conduct its own due diligence before entering into a Patent License Agreement.
OTC chooses a licensee based on a company’s ability to commercialize the technology for the benefit of the general public. Generally, OTC requires a business plan or product development plan from the potential licensee. Sometimes an established company with experience in similar technologies and markets is the best choice for a particular technology. In other cases, the focus and intensity of a startup company is a better option.
LICENSE THE INVENTION
Here are the OTC sample Patent License Agreements and the User Guide.
OTC has endorsed the Association of University Technology Manager’s (AUTM) list of points to consider as companies license inventions from a university.
AUTM’s Points to Consider:
- Universities should reserve the right to practice licensed inventions and to allow other non-profit and governmental organizations to do so.
- Exclusive licenses should be structured in a manner that encourages technology development and use.
- Strive to minimize the licensing of “future improvements”
- Universities should anticipate and help to manage technology transfer related conflicts of interest.
- Ensure broad access to research tools.
- Be mindful of export regulations.
- Consider including provisions that address unmet needs, such as those of neglected patient populations or geographic areas, giving particular attention to improved therapeutics, diagnostics and agricultural technologies for the developing world.
DEVELOP THE PRODUCT
Licensees are welcome to continue the collaboration with UTEP by sponsoring research projects in the inventor’s lab. If you have questions about sponsored research, please contact UTEP’s Research & Innovation (R&I).
OTC works closely with ORSP on IP issues in Sponsored Research Agreements. UTEP generally retains ownership of patent rights and other intellectual property resulting from sponsored research. However, the sponsor may have rights to negotiate a license to the IP resulting from the research. The sponsor generally will not have contractual rights to discoveries that are outside of the scope of the research or that were invented prior to the research term. Therefore, it is important to define the scope of work within a research agreement and to review the IP provisions in the research contract.
Many licensees require the active assistance of the inventors to facilitate their commercialization efforts. UTEP employee’s participation with a startup or any consulting arrangement with a licensee is governed by UTEP conflict of interest policies. UTEP conflict of interest policies and online reporting portal can be found here.